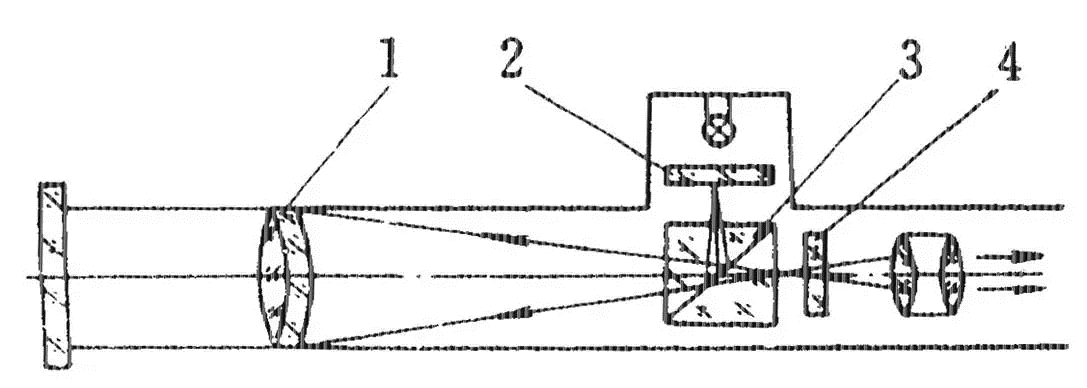
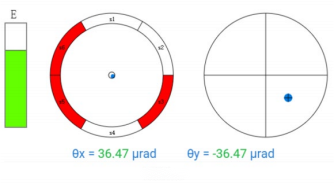
Semiconductor Diodes
Light Sources
Optical Accessories
Fiber Accessories
PhotoDetectors
Optical analysis device
Optical Imaging
Optomechanics
Applications
VCSEL Laser Diode
| 600-700nm VCSEL laser diode
| 700-750nm VCSEL laser diode
| 750-830nm VCSEL laser diode
| 830-870nm VCSEL laser diode
| 870-900nm VCSEL laser diode
| 900-1200nm VCSEL laser diode
| 1200-1350nm VCSEL laser diode
| 1350-1500nm VCSEL laser diode
| 1500-1600nm VCSEL laser diode
| 1600-1700nm VCSEL laser diode
Coherent Sources
| Single frequency laser
| Fiber coupled laser source
| Miniature laser module
| He-Ne laser
| Fiber laser
| Mid-IR laser Ready-to-use
| Mode-locked laser
| 1550nm NL single frequency laser
| Photon-light source association
| 532nm solid-state laser
| Semiconductor fab
| Mid infrared laser
| Solid-state laser
| Pump light source
Incoherent Sources
| Broadband Light Source/Illuminator
| Laser pumped phosphor broadband light source
| Erbium fiber ASE source
| Thulium fiber ASE source
| Ytterbium doped fiber ASE light source
| Dysprosium doped fiber ASE light source
| LED light source
| SLD light source
| Praseodymium doped fiber ASE light source
| Thermal IR light source
| He-Ne laser
Optical System
| Objective ,scanning & Tube lens
| Beam expander
| Camera lens
| Fly eye homogenizer
| Chromatic aberration correction
| LD Collimation & Focusing Tubes
| Galvanometer system
| Adaptive optics components
| Dispersion measurement system
| Single/multi-pass gas cells
| Photoacoustic spectroscopy
| Portable Raman Spectrometer
| Cage/Lens Tube Mounted Optics
| Shear interference
| Soleil Babinet compensator
| Integrated subsystem
Active devices
| EOM
| AOM
| High-speed transmitter/receiver
| Phase stabilizer
| Optical reference cavity
| Tunable narrowband Fabry Perot filter
| Liquid crystal tunable filter
| Spatial Light Modulator
| LCD products
| Birefringent system
| MEMS grating modulator
| Deformable mirror
| Adjustable focus lens
| Polarimeter
Optical Kits
| N-BK7 spherical lens set (installed)
| UV fused silica spherical lens set (installed)
| N-BK7 spherical lens set (not installed)
| Achromatic double laminated lens kit
| Aspherical lens kit
| Scattering film set
| ND filter kit
| Color filter kit
| Bandpass filter kit
| Hard-Coated Edgepass Filter Kits
| Precision Pinhole Kits
| Optical assembly kit
Fiber & patch cords
| Single-mode fiber
| PM single-mode fiber patch cord
| Multimode fiber bundle
| Custom fiber patch cord
| SM Fiber
| MM Fiber
| PM fiber
| Fluoride Fiber
| SM Polarization Fiber
| Rotating fiber
| High Non-Linear Fiber
| Double clad fiber
| Rare-earth doped fiber
| PCF fiber
| Coreless terminal fiber
| Fiber optic customization
| 2-in-1 PM patch cord
| SM Fiber Connector
| hollow fiber
| Multimode fiber jumper
| Metalized optical fiber
Fiber Optic Euipments
| Fiber optic table components &systems
| FiberPort collimator/coupler
| Fiber coupling platform
| Adjustable fiber coupler
| Optical fiber adapter
| L-Type Mating Tube
| Fiber optic compression block
| Fiber clamp with vacuum port
| Fiber head mounting bracket
| Collimator adapter
| FiberPort base
| Adjustable collimator adapter
| Mini collimator base
| MM Fiber filter cube, removable
| Cuvette holder
| MM Fiber filter mount, embedded
| 1x1 fiber rotary connector
| 1x2 fiber rotary splitter
| Rotary joint patch cord
Fiber optic components
| Fiber collimator
| Fiber coupler/splitter
| Fiber Optic WDM
| Circulator
| Fiber retroreflector
| Pump Combiner
| MM Fiber combiner
| Fiber polarization control component
| Fiber isolator
| Fiber attenuator
| Fiber optic filter
| UHV fiber feedthrough flange
| Optical fiber adapter
| Optical switch
| interferometer
| Patch Cord
| Fiber lab supplies
| Etalon
| Mode Divison Multiplexers
| Mode Field Adaptor
| optical delay line
| fiber optic phase modulator
| Space Division Multiplexing Components
Power and Energy Meters
| Photodiode Power Meter Sensors
| Thermal Optical Power Meter Sensor
| Thermal Position and Power Sensors
| Pyroelectric Energy Meter Sensors
| Digital handheld power meter sensors
| Multi-touch power meter probe sensors
| Analog handheld power meter
| Dual-channel power meter
| USB optical power meter
| Power meter kit
| Wireless power meter ,with sensor
| Miniature USB power meter
| Fiber power meter
| Power Meter Tutorial
| Integral ball
| Near-IR power meter
Imaging system
| Microscope System Overview
| Multiphoton Microscope
| Veneto inverted microscope
| Prelude imaging microscope
| Miniature two-photon microscope
| Multiphoton mesoscopic microscope
| OCT Imaging System
| Cerna Modular Microscope Platform
| Confocal system
| Birefringent microscope
| Birefringent system
| Microscope accessories
| Microscope software
| Tunable Ti:Sapphire femtosecond laser for multiphoton imaging
Imaging components
| Life Science & Microscope Optomechanics
| Microscope optical components
| Cerna wide-field & electrophysiological devices
| DIY confocal/laser scanning components
| High-speed modulators
| High speed modulator and attenuator
| Sample holder
| Microscope platform
| Light Sources
| Piezoelectric Microscope Objective Shifter
| Z-axis Piezoelectric Stage for Microscope Slides
| Microscope Vibration Isolation Table
| Laser scanning scope
Camera
| Microscope Camera selection guide
| CMOS microscope camera (1.6M pixels)
| MOS microscope camera (1.3-12.3M pixels)
| 5MP CMOS polarization camera
| SCMOS microscope camera (2.1M pixels)
| Camera, lens kit & Mounting base
| Camera terminology introduction
| Camera Noise Tutorial
| Customized/OEM Microscope Camera
| Camera software download
| UV camera
| Near infrared camera
| Mid infrared camera
| CMOS camera
Optogenetics
| Customized Optogenetic Solutions
| Overview of fiber optic photometry
| Optical fiber needle
| Needle implantation guide head
| Needle holder & adapter
| Optogenetic patch cord
| Rotating fiber optic patch cord
| 1x1 rotary connector
| 1x2 rotating fiber connector/splitter
| Interconnects and matching tubes
| Optogenetics driver kit
| Stainless steel & ceramic ferrules
| Optogenetics 2x2 couplers/beamsplitters
| MM Fiber filter cube, removable
| Fluorescent imaging filter kit
| Fiber coupled LED
| 473 nm fiber-coupled laser for optogenetics
Optical Mechanical Components
| Optical Posts Components
| Lens tube
| Adapter
| Mounting rack
| Cage system
| Mounting/Angle Bracket
| Optical guides
| Polaris ® Product Line
| Mini series opto-mechanical components
| Aperture
| Optical casing
| Vacuum components
| Instrument rack
| Optomechanical instruments
| Optomechanical equipment manufacturing
Spectroscopy
| Spectrometer and signal detector
| IRsweep spectrometer
| Photoacoustic Spectroscopy
| Broadband Sources & Spectral Lamp
| Single wavelength light sources
| Spectroscopy optical components
| Integrated subsystems for spectroscopy
| Pure air circulation device
| Spectroscopy sample container
| Multimode sample fiber bundles
| Transient absorption spectroscopy teaching kit
| Spectrometer teaching kit
| Complete incoherent light source product line
| Coherent light source product line
Quantum technology
| Single photon light source
| Single photon detection
| Single photon counting module
| Balance detector
| Diamond with NV center
| Polaris@Mount
| Piezoelectric interia vacuum displacement table
| Optical reference cavity with crystal film mirror
| Tunable Fabry Perot filter, narrowband pass
| Ready to use Ultra-low noise laser
| Vacuum components
| Sealed steam reference cell
| Quantum Optics Teaching Kit
| Quantum Erase Kit
| Quantum Encryption Suite
OEM/Manufacturing Capability
| OEM promotional brochure
| Customized/OEM scientific grade camera
| Desktop case production capacity
| Piezoelectric ceramic product production line
| OEM OCT system
| Semiconductor fab
| Fiber optic component manufacturing
| Elliptec technology for OEM
| Motion control equipment manufacturing
| OEM Photonics Services
| Anodizing production capacity
| Optical processing
| Optomechanical manufacturing processes
| Platform & breadboard manufacturing capability
| Optical fiber manufacturing